Your team shouldn’t be overwhelmed by manual fixes, rejected invoices, or audit stress when managing ZATCA e-invoicing and VAT compliance. The right ERP system can simplify these tasks, but not every solution fits Saudi Arabia’s legal framework or meets the country’s practical ERP requirements.
Many global ERPs lack local tax logic or are slow to adjust to ZATCA’s updates. The result can be rejected invoices, delayed payments, penalties, and manual workarounds that increase audit risk and reduce customer trust. For companies involved in KSA’s growing portfolio of megaprojects, such inefficiencies can also affect cash flow and project delivery timelines.
This article outlines the essentials of ZATCA compliance, explains the ERP system requirements necessary to meet VAT and e-invoicing standards, and shares practical steps to help you stay compliant as Saudi regulations continue to evolve.
ZATCA E-Invoicing: Regulatory Context
Saudi Arabia’s e-invoicing mandate,
FATOORA, was introduced by the
Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) to standardize invoicing, improve compliance, and minimize opportunities for tax evasion. The framework is being implemented in two phases, with
each phase introducing additional technical and compliance-related ERP requirements.
Phase 1: Generation Phase
Since December 4, 2021, businesses have been required to issue and store invoices electronically in structured formats, such as XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML.
Under Phase 1, this obligation applies to most business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-government (B2G) transactions, for which invoices must be generated electronically through a compliant solution.
Key points include:
-
Mandatory fields. Invoices must include the data elements listed in Article 53(5) of the VAT Implementing Regulations and Annex 2 of the E-Invoicing Resolution.
-
Compliant software. Invoices must be produced using an E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) approved by ZATCA. Scanned, copied, or manually digitized paper invoices are not considered compliant.
-
Flexible format. While invoices must be electronic, ZATCA does not prescribe a technical format at this stage. Delivery to buyers can be in any electronic form.
This phase primarily focused on preparing businesses for digital invoicing by ensuring that invoices were generated electronically and contained all required fields.
Phase 2: Integration Phase
Since January 2023, businesses have been gradually required to integrate their systems with ZATCA’s platform in order to transmit invoice data in real time.
Phase 2 builds on the Generation Phase by adding structured formats, clearance requirements, and mandatory system integration.
The ERP requirements are as follows:
-
Structured format. Invoices must be generated in XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML).
-
Real-time clearance. For B2B and B2G transactions, invoices must be submitted in XML format via API to the ZATCA FATOORA platform. The platform validates the invoice, applies a cryptographic stamp and QR code, and returns the cleared XML to the business.
-
Buyer presentation. Once cleared, invoices must be shared with buyers in XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML, ensuring both human-readable and machine-readable formats.
Through this phase, e-invoicing becomes a real-time integration with the tax authority, embedding traceability and security directly into financial transactions.
Core ERP Requirements for ZATCA Compliance
ZATCA-approved ERP systems are designed to make compliance straightforward. If you are using ERP software that meets ZATCA’s technical and security standards, your invoicing process will automatically follow the required format, content, and verification rules. This helps you stay compliant without constant manual checks.
Invoice Generation in Correct Format
Under ZATCA regulations, all e-invoices must be issued in XML format. This requirement applies to both B2B and B2C transactions, although each follows a slightly different process.
B2B invoices follow the clearance model, in which they are sent to ZATCA for approval before being shared with the buyer. B2C invoices follow the reporting model and must be reported to ZATCA within 24 hours of issuance.
When you share tax invoices with buyers, they can be sent in XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML. For B2C sales, invoices must be provided in paper form. If both parties agree, they can also be shared electronically in a readable format.
Quick check
Make sure your ERP system can automatically generate invoices in XML and export them in PDF/A-3 format for sharing. This keeps you compliant under both clearance and reporting models.
Mandatory Data Fields and Technical Elements
Every invoice you generate must contain key identifiers and security fields that ensure accuracy and traceability. Your ZATCA approved software should automatically create and embed these fields into the XML file.
The identifiers can be:
-
UUID (Universally Unique Identifier). A unique 128-bit number is assigned to each invoice. It prevents duplication and ensures every invoice can be traced individually.
-
Hash. A digital fingerprint that confirms the invoice has not been altered. Even a small change to the data will produce a completely different hash value.
-
QR Code. A scannable code printed on the invoice that allows ZATCA or your customer to verify its authenticity instantly.
If your ERP or other ZATCA-approved software generates these fields automatically, you will avoid manual errors and maintain data integrity across all transactions.
Quick check
Always use an e-invoicing solution that handles UUIDs, hashes, and QR codes automatically. These technical details are what make your invoices verifiable and compliant.
Integration Capability with ZATCA’s FATOORA Platform
To stay compliant, your VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA requirements must be properly connected to this platform so every invoice or credit or debit note is submitted in real time.
To ensure smooth operation, your ERP should include:
-
API integration. Direct communication with ZATCA’s API for instant invoice clearance and reporting.
-
Internet connectivity. A stable, continuous internet connection for live data exchange. The system should retry automatically if a submission fails.
-
Error handling. Tracking failed submissions, logging them, and resending automatically once the connection is restored.
With these features in place, you can be confident that your invoices reach ZATCA correctly every time.
Quick check
Check your API and submission logs regularly. This helps you detect transmission errors early and maintain uninterrupted compliance.
Security, Data Integrity and Audit Trail
ZATCA requires ERP systems to keep financial data secure and tamper-proof.
To meet these ERP requirements, your software should include the following features.
-
Tamper-proof controls. Lock invoice counters and system dates to prevent backdating or unauthorized edits.
-
Audit trail. Keep a detailed, uneditable log of all invoice activities, including creation, modification, and clearance.
-
Cryptographic key management. Protect the encryption keys used to secure and sign your invoices.
If your VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA includes these ZATCA compliant features, your invoice data will remain accurate, protected, and auditable.
Quick check
Run periodic checks on your audit logs and user permissions. Detecting unusual activity early helps you prevent compliance risks.
Archival and Retrieval of E-Invoices
ZATCA requires that every structured e-invoice file, such as XML or PDF/A-3, is digitally archived within Saudi Arabia. Your VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA should store these files securely and make them easy to retrieve for audits or reviews.
To meet compliance, the archive must follow several technical standards:
-
Naming convention. Each file must follow a consistent and traceable naming pattern.
-
Non-tampering. Once archived, invoices cannot be changed or deleted.
-
Non-repudiation. The system must prove that the data came from an authorized source and has not been altered.
Keeping your archive in a Saudi-based environment is a legal requirement that protects sensitive financial information.
Quick check
Test your ERP’s retrieval functions regularly. Being able to locate and produce an invoice quickly during a ZATCA audit is one of the best signs of compliance.
Multi-Language, Multi-Currency, and Multi-Entity Support
If your organization operates across regions, your VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA should be flexible enough to support multiple configurations. ZATCA requires invoices to be issued in Arabic, but bilingual invoices in Arabic and English are often used to make communication easier for clients and partners.
Your ERP should also handle multiple currencies for international transactions and multiple legal entities within the same organization. Each entity’s tax data must remain separate and traceable.
This flexibility allows you to manage regional operations without risking reporting errors or compliance issues.
Quick check
Always verify that the Arabic version of each invoice matches the English version. The Arabic copy is the official record recognized by ZATCA.
Scalability and Performance
As your operations grow, the volume of invoices your KSA VAT‑compliant ERP system must process increases. ZATCA compliance remains the same for all businesses. Whether you issue a few invoices or thousands, each one must follow the same standards.
Your VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA should be capable of handling high transaction volumes without delay or data loss. It should also support batch processing to generate and submit multiple invoices efficiently.
Scalable performance ensures that compliance remains consistent even during busy periods such as month-end closings or project handovers.
Quick check
Monitor system performance during high activity. Slow processing or submission delays can cause missed deadlines and potential non-compliance.
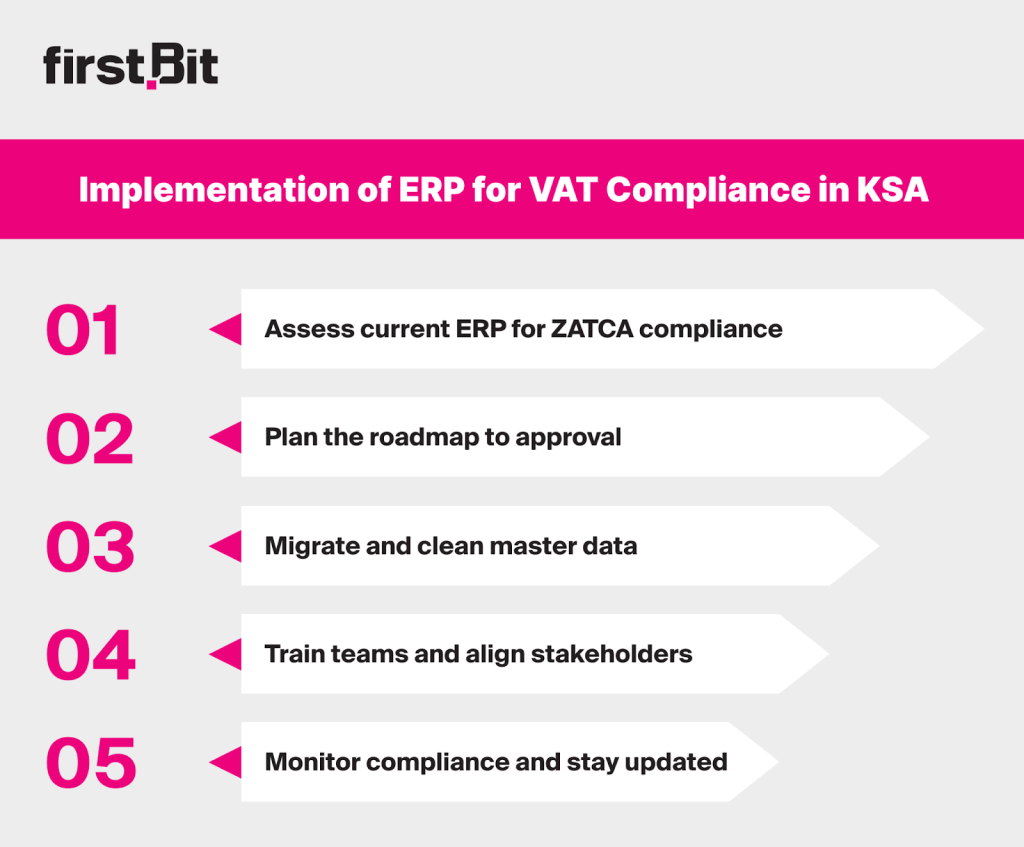
Implementation of ERP for VAT Compliance in KSA
Implementing a VAT‑compliant ERP for KSA in Saudi Arabia starts with assessing your current setup, planning a roadmap, preparing clean data, training your team, and staying alert to future updates.
Implementation of ERP for VAT Compliance in KSA
Assess Existing ERP Capabilities to Meet ZATCA ERP System Requirements
Start by reviewing your KSA VAT‑compliant ERP system against ZATCA’s e-invoicing requirements. Check if it can issue invoices in XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML, integrate with the FATOORA platform, and include all mandatory data fields and security features.
This assessment helps identify any functionality gaps early.
Define the Roadmap to ZATCA Approved Software
Once you know what’s missing, outline a clear implementation plan. This should include:
ZATCA’s phased rollout means your ERP must be technically ready and aligned with the authority’s schedule.
Start Data Migration and Master Data Hygiene
Accurate data is essential for generating compliant invoices. Make sure seller and buyer tax IDs, VAT registration numbers (TRNs), and all customer and supplier details are correct. Even small errors in this data can lead to invoice rejection or compliance risks.
Organize Training and Stakeholder Engagement
Technology alone isn’t enough. Finance teams must know how to issue and manage compliant invoices. IT must handle system integration and archiving. Auditors or internal controls should monitor compliance and exceptions. Regular training keeps all stakeholders aligned and reduces human error.
Monitor Progress and Be Ready for Future Update
ZATCA continues to expand Phase 2 in waves, so ERP system requirements may evolve. Keep an eye on system performance and integration stability, monitor official updates, and ensure your ERP remains aligned with the latest technical standards.
Best Practices for ERP VAT Compliance in KSA
The most effective companies make compliance part of daily ERP routines. Here, you’ll find simple, practical steps to help your business stay aligned with ZATCA’s VAT and e-invoicing rules.
Best Practices for ERP VAT Compliance in KSA
Automate Invoice Generation and Submission Workflows
Set up your KSA VAT‑compliant ERP system to automatically create, clear, and report invoices in real time. All invoices should be generated in XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) and sent to the FATOORA platform. Scheduling background jobs for data syncs helps avoid submission delays.
Enforce Validation and Approval Controls
Embed validation rules in your ERP system to check for mandatory data, such as seller and buyer details, VAT rates, totals, UUIDs, and QR code submissions. Add approval steps so that finance managers can only review invoices after all fields have passed validation.
Maintain Clear Audit Logs and Change Histories
A traceable record should be left for every action, whether that be creation, editing, submission or correction. Enable system logging to preserve an unaltered audit trail. ZATCA requires full traceability to confirm the authenticity of invoices and prevent tampering.
Conduct Regular Compliance Reviews and System Health Checks
Review your ERP’s connection with ZATCA’s APIs regularly to ensure stable submissions and correct timestamps. Periodically test your archive, API tokens, and configurations to prevent technical gaps before they affect compliance.
Leverage Vendor/Partner Ecosystem
Collaborate with KSA VAT‑compliant ERP vendors and certified partners that provide ZATCA-approved compliance modules or add-ons. Vendors already integrated with FATOORA can help maintain alignment with evolving technical ERP requirements. Systems like FirstBit ERP are designed to support VAT and e-invoicing standards in Saudi Arabia, helping businesses stay consistently compliant.
How FirstBit Meets All ERP System Requirements for VAT Compliance
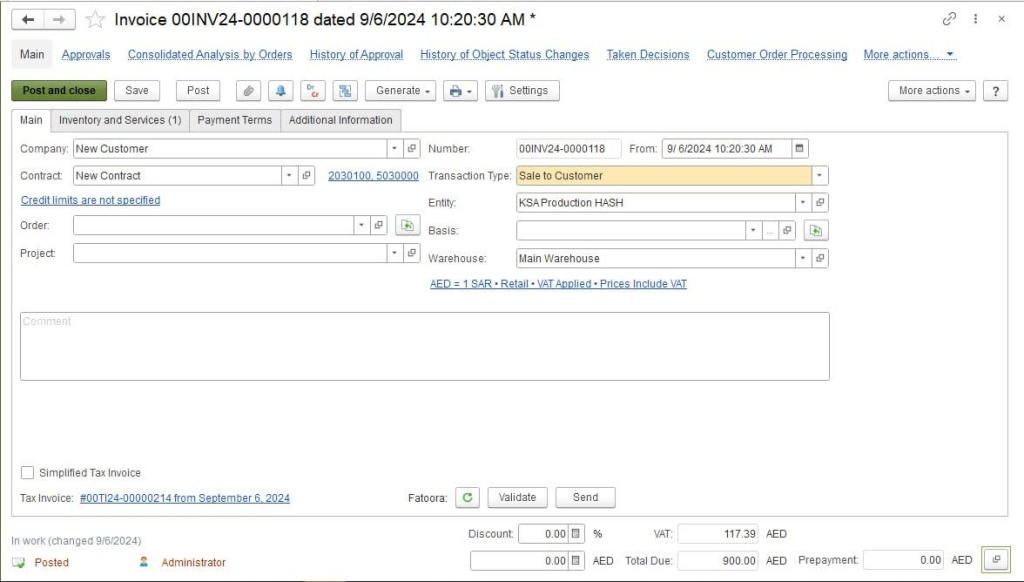
FirstBit ERP is designed to align with ZATCA requirements. It supports structured e‑invoice generation, secure data handling, and seamless API connectivity with the FATOORA platform.
Invoice creation in FirstBit ERP
The system also enables automatic validations, bilingual (Arabic/English) invoice issuance, and secure in‑kingdom archiving.
By combining configurable approval workflows, real-time monitoring, and detailed audit logs,
FirstBit ERP supports continuous VAT and e‑invoicing compliance as ZATCA requirements evolve in KSA.
FAQ
Is FirstBit ERP compliant with ZATCA e-invoicing requirements?
Yes. FirstBit ERP is fully aligned with ZATCA’s e-invoicing framework, including Phase 2 (integration phase). The system automatically generates structured invoices, applies digital signatures and QR codes, and integrates directly with the FATOORA platform for clearance and reporting.
Can FirstBit handle VAT-compliant invoicing for construction projects?
Yes. The system creates VAT-compliant invoices based on project progress, contract terms, and milestone billing. Each invoice meets ZATCA’s data, formatting, and validation requirements, ensuring accuracy and compliance without manual adjustments.
Is payroll in FirstBit ERP compliant with Saudi labor laws?
Yes. The payroll module is built to reflect KSA labor regulations. It calculates salaries, overtime, and deductions automatically, synchronizes with attendance data, and ensures wage payments comply with the Wage Protection System (WPS).
How does FirstBit ERP support audit readiness and tax transparency?
FirstBit ERP maintains secure, traceable records for every invoice and transaction. All documents include XML and PDF copies, digital stamps, and full audit trails. This ensures that your company can instantly retrieve verified records during any ZATCA inspection or financial review.
Anna Fischer
Construction Content Writer
Anna has a background in IT companies and has written numerous articles on technology topics. Now, building up her expertise in construction and legal regulations, Anna expands the horizons of our blog and delights her readers with insightful articles.